Junhyun Park
I am a master student at DGIST, advised by Prof. Minho Hwang. I received my Bachelor's degree in Computer Science and Electronic Engineering from DGIST in 2024.
During my undergraduate studies, I had the privilege of being advised by Prof. Minho Hwang at DGIST as an undergraduate researcher. Additionally, I was advised by Prof. Synho Do and Prof. Kyungsu Kim during my internship at Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital.

News
- [June 2025] Exciting news! Our paper OFF-CLIP: Improving Normal Detection Confidence in Radiology CLIP with Simple Off-Diagonal Term Auto-Adjustment has been early accepted to MICCAI (top 9%). In addition, our paper Vibration-Assisted Hysteresis Mitigation for Achieving High Compensation Efficiency has been accepted to IEEE IROS. I am honored to be the first author on both papers.
- [March 2025] I will be attending IEEE ICRA 2025 to present my paper, "Hysteresis Compensation of Flexible Continuum Manipulator Using RGBD Sensing and Temporal Convolutional Network." Looking forward to meeting everyone—let’s grab a coffee and chat.
- [May 2024] Our paper "Hysteresis Compensation of Flexible Continuum Manipulator using RGBD Sensing and Temporal Convolutional Network" has been accepted to IEEE RA-L!
- [April 2024] Our paper "Integrating ChatGPT into Secure Hospital Networks: A Case Study on Improving Radiology Report Analysis" has been accepted to CHIL 2024!
Research
I am interested in robotics, deep learning, biomedical engineering, and robot automation. My ultimate research goal is to develop fully automated surgical robots, including diagnostic automation. In this vision, AI analyzes a patient's X-ray, MRI, or other medical images to detect anomalies and plan the surgery. Using this diagnosis, a continuum manipulator—leveraging its scar-free advantages—would navigate through natural orifices to perform the procedure autonomously. This represents the future I strive to achieve in my research.
* states the Equal Contribution
|
Surgical Robotics
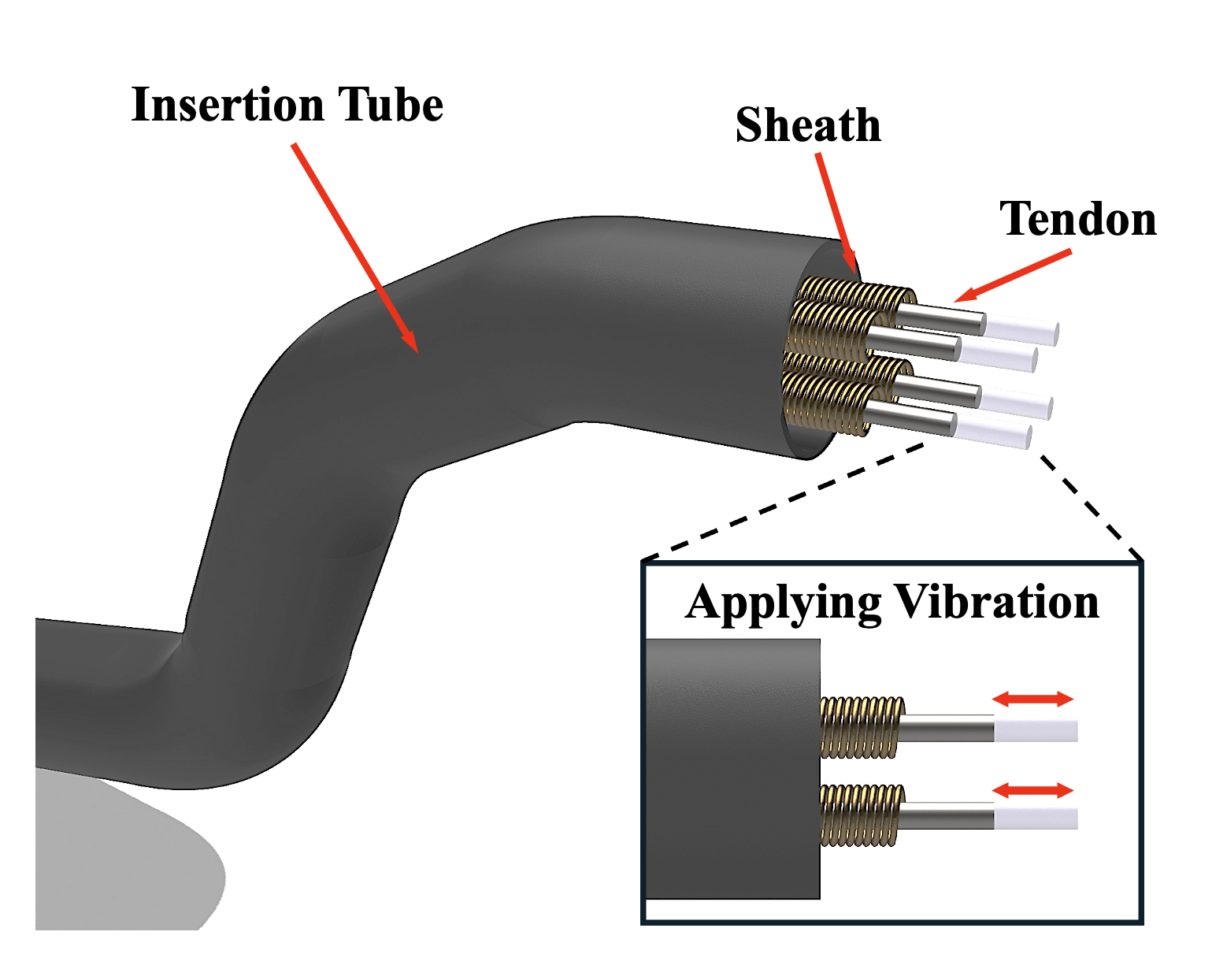
Vibration-Assisted Hysteresis Mitigation for Achieving High Compensation Efficiency
Myeongbo Park*, Chunggil An*, Junhyun Park*, Jonghyun Kang, Minho Hwang IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) , 2025 arXiv We introduce a vibration-assisted hysteresis compensation method for tendon-sheath mechanisms. Controlled vibration reduces friction and dead zones, improving trajectory tracking. Combined with DL based hysteresis compensation methods, 85% hysteresis decreases. |
|
Medical AI
Diagnosis Automation
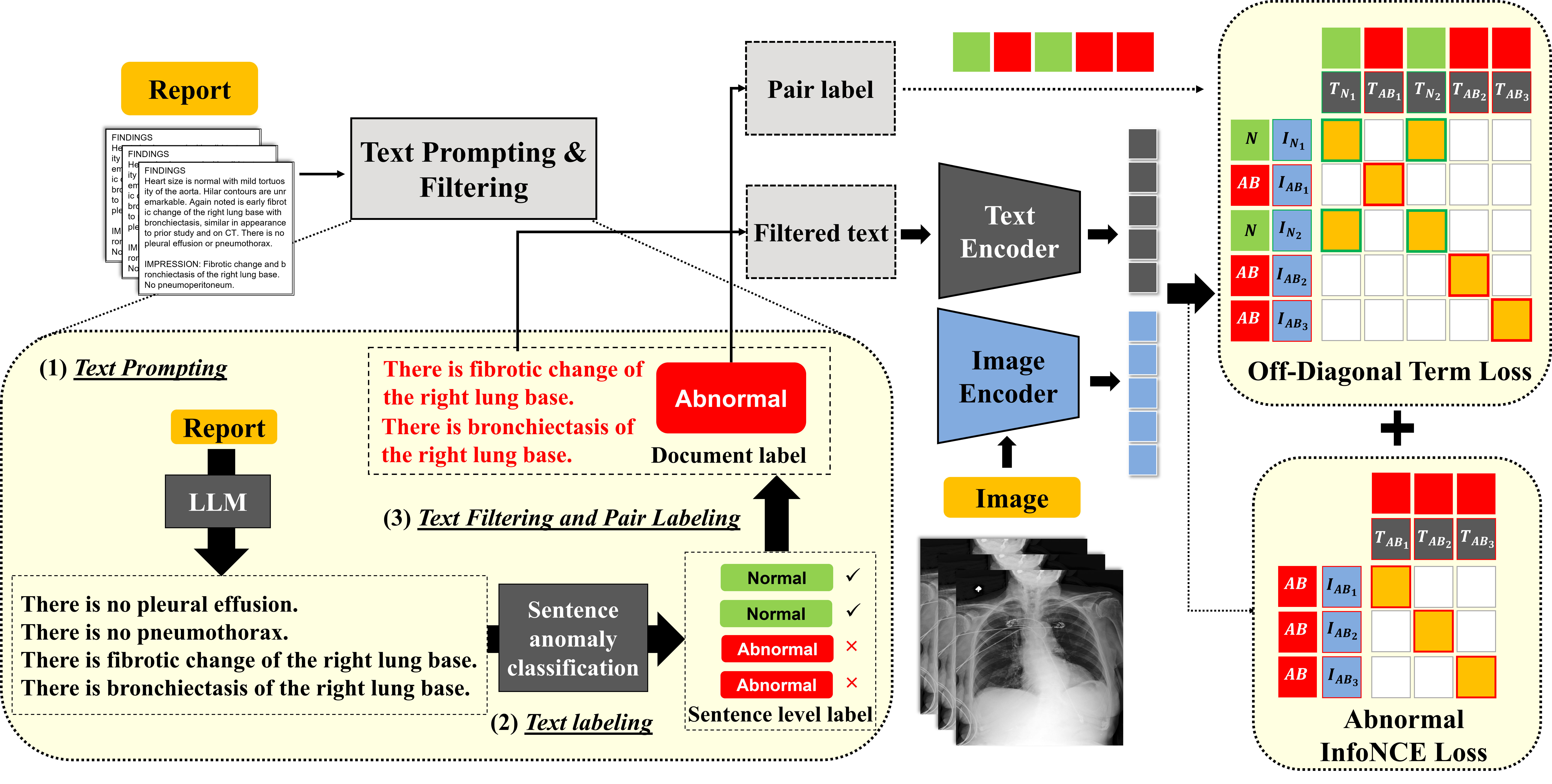
OFF-CLIP: Improving Normal Detection Confidence in Radiology CLIP with Simple Off-Diagonal Term Auto-Adjustment
Junhyun Park*, Chanyu Moon*, Donghwan Lee, Kyungsu Kim, Minho Hwang Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) , Early Accepted , 2025 Top 9% Publication with Early Acceptance Top Medical AI Conference (Acceptance Rate: 30%) arXiv OFF-CLIP utilizes off-diagonal loss and sentence-level text filtering to improve normal detection and reduce false negatives. Enhancing zero-shot classification performance and anomaly localization. |
|
Surgical Robotics
Surgery Automation
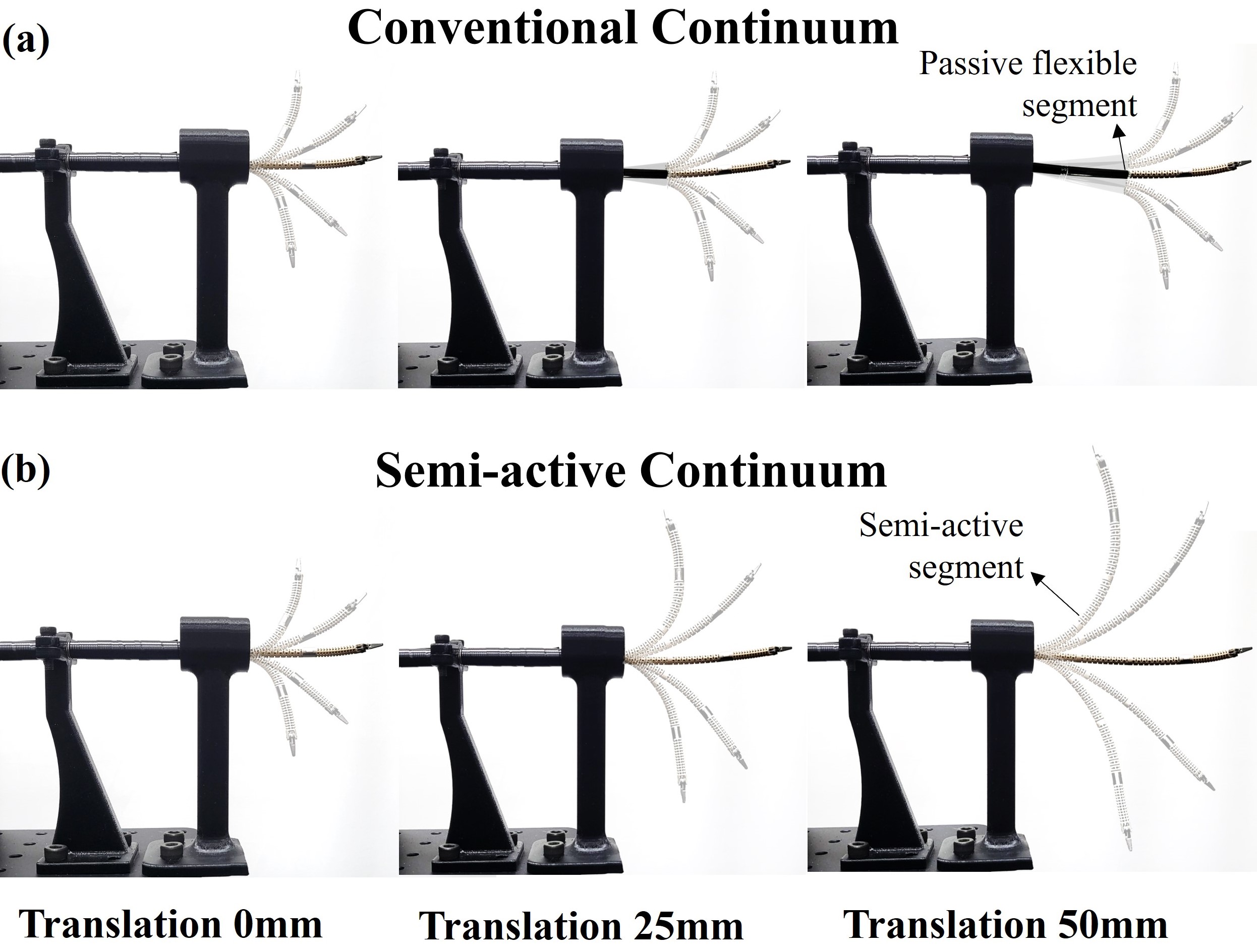
SAM: Semi-Active Mechanism for Extensible Continuum Manipulator and Real-time Hysteresis Compensation Control Algorithm
Junhyun Park*, Seonghyeok Jang*, Myeongbo Park, Hyojae Park, Jeonghyeon Yoon, Minho Hwang The International Journal of Medical Robotics and Computer Assisted Surgery (IJMRCAS) , 2024 Paper / Video / arXiv This study present an extensible cable-driven continuum manipulator with a semi-active mechanism (SAM) and a TCN-based real-time hysteresis compensation algorithm. SAM improves lesion access, while TCN-based compensation enhances accuracy, potentially improving surgical performance |
|
Surgical Robotics
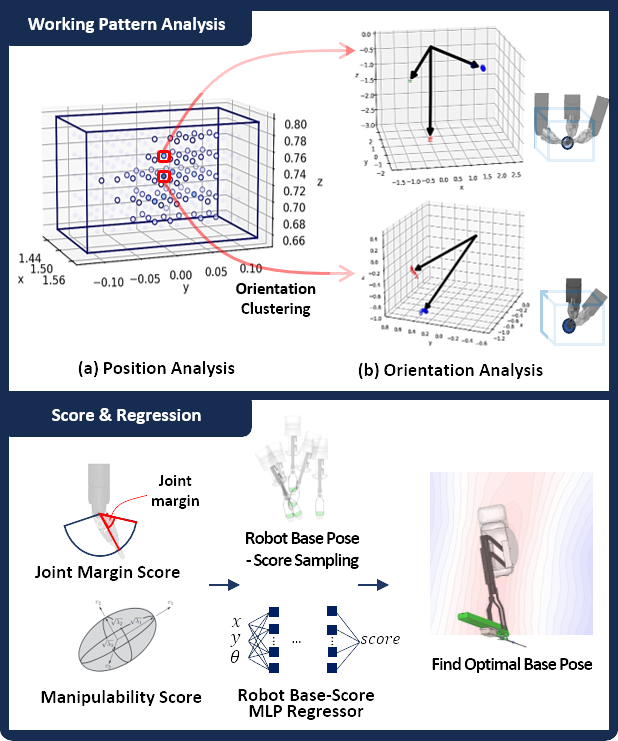
Optimizing Base Placement of Surgical Robot: Kinematics Data-Driven Approach by Analyzing Working Pattern
Jeonghyeon Yoon* Junhyun Park*, Hyojae Park, Hakyoon Lee, Sangwon Lee, Minho Hwang IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) , 2024 Paper / Video / arXiv This study introduces a machine learning approach to determine the best base pose based on the surgeon’s working pattern. By clustering recorded end-effector poses, key positions are identified, and scoring metrics address joint limits and singularities. |
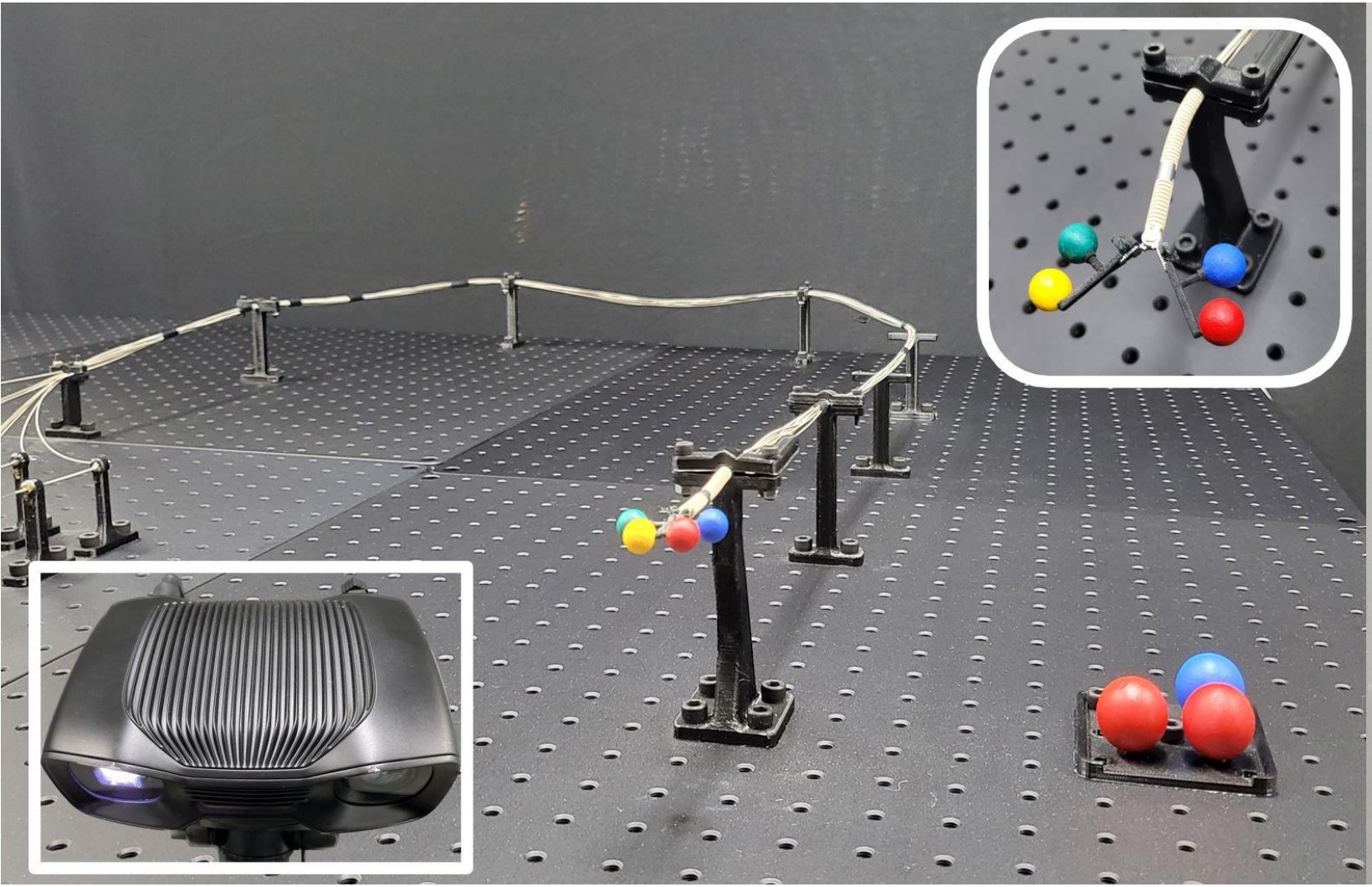
|
Surgical Robotics
Surgery Automation
Hysteresis Compensation of Flexible Continuum Manipulator using RGBD Sensing and Temporal Convolutional Network
Junhyun Park*, Seonghyeok Jang*, Hyojae Park, Seongjun Bae, Minho Hwang IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L) , 2024 Paper / Video / arXiv This letter proposes a data-driven approach based on TCN to capture these nonlinear and previous states-dependent characteristics of cable actuation. Leveraging trained TCNs, we build a control algorithm to compensate for hysteresis. Tracking tests in task space using unseen trajectories show that the proposed control algorithm reduces the average position and orientation error by 61.39% (from 13.7 mm to 5.29 mm) and 64.04% (from 31.17◦ to 11.21◦), respectively. |
|
Medical AI
Diagnosis Automation
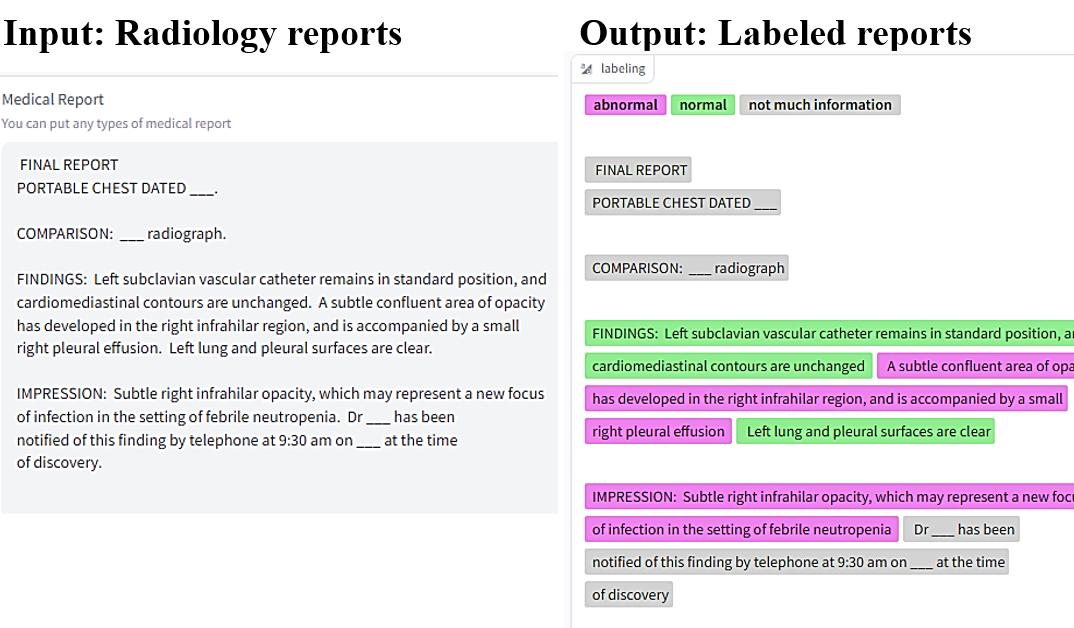
Integrating ChatGPT into Secure Hospital Networks: A Case Study on Improving Radiology Report Analysis
Kyungsu Kim*, Junhyun Park*, Saul Langarica, Adham Mahmoud Alkhadrawi, Synho Do Conference on Health, Inference, and Learning (CHIL), 2024 Top Medical AI Conference (Acceptance Rate: 34%) Paper / Huggingface / arXiv / Github This study demonstrates the first in-hospital adaptation of a cloud-based AI, similar to ChatGPT, into a secure model for analyzing radiology reports, prioritizing patient data privacy. By employing a unique sentence-level knowledge distillation method through contrastive learning,we achieve over 95% accuracy in detecting anomalies. |